EQTEC Advanced Gasification Technology
Innovation excellence
Our team applies decades of experience with gasification and syngas in both R&D and commercial environments. Led by four PhDs in Chemical Engineering, we are at the forefront of syngas production, applying end-to-end process engineering as well as design and mechanical, electrical and civil engineering for the deployment of EQTEC’s unique technologies.

R&D installation at Universite de Lorraine, France
The proof in our innovation capability is in the gasification plants we have built and are building. But our drive for commercial execution is matched by our dedication to continuous innovation and development of new intellectual property (IP) and new patents. On our own sites and also in collaboration with R&D partners, our expert engineers are continuously testing the limits of our advanced gasification capabilities and delivering our technology roadmap.
Leading gas engine company Jenbacher has given our technology special commendation for the purity of the syngas it produces and for the reliability and efficiency of the equipment.
At the University of Lorraine (France) and University of Extremadura (Spain), working with their experts, we have installed gasification equipment and operate R&D pilot plants. We actively invest in maintenance, upgrade and application of these facilities, enabling us to identify, test – we now have a proprietary library with nearly 60 different feedstocks analysed – and expand into areas of emerging market interest.
In Gallina (Italy), our Italia MDC (Market Development Centre) is converting wood waste into electrical power for export to the national grid and is producing biochar. The plant demonstrates EQTEC technology in a live, commercial environment and shows our agricultural solution model which demonstrates the potential for smaller-scale, autonomous plants in remote areas to convert agricultural and forestry biomass into value for the local community.
Our practical know-how combines with our patents and other IP and we work closely with the following partners, to further our technical expertise and ensure we continue to set the global innovation standards for advanced gasification. We maintain a number of patents around the world for multiple elements of its technology and we continuously reviews opportunities for establishing new patents where we have a unique contribution to advanced gasification.
Less wasteful than landfill, cleaner than incineration
Sustainably converting waste into types of baseload energy and biofuels is the next best option after reducing, reusing and recycling what is recyclable. But not all forms of waste management – even those intended to support a circular economy – are equal. Most of the waste not recycled is sent to landfill or incinerated. These methods aren’t sustainable and they aren’t good for the environment or good for communities.
Gasification: key facts
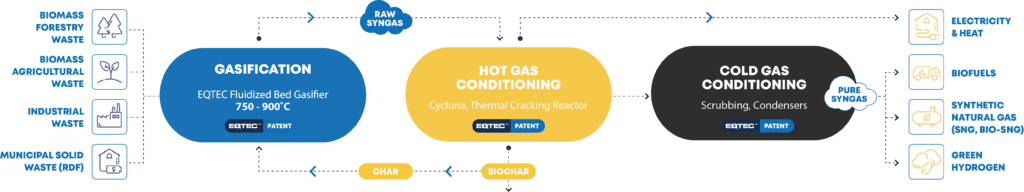
Gasification is the process of thermochemically converting feedstock such as RDF, agricultural, biomass and industrial waste and plastics into syngas. Syngas is then used as fuel to generate electricity and heat, or as a commodity, to produce transportation fuels, Synthetic Natural Gas (SNG) and hydrogen.
The US Department of Energy defines gasification as
“A process technology that is designed and operated for the purpose of producing synthesis gas (a commodity which can be used to produce fuels, chemicals or power) through the chemical conversion of carbonaceous materials.”
Advanced gasification is a thermochemical process characterised by the purity of the synthesis gas (‘syngas’) it produces, the operational plant availability it supports and the commercial opportunities this creates…all without applying combustion and with a very clean CO2 and emissions profile.
Cuts down on waste sent to landfill
Is more efficient than other waste-to-value methods
Cuts carbon dioxide, methane, hydrofluorocarbons, tropospheric ozone and nitrous oxide emissions associated with incineration
Helps waste owners, developers and contractors to meet or exceed increasingly stringent environmental regulations
Produces only non-hazardous ashes as a by-product, resulting in a significantly lower carbon footprint compared with other waste-to-energy methods
Eliminates the health hazards associated with burning waste.
EQTEC technology: the patented process
Our Advanced Gasification Technology is based on a bubbling fluid bed gasifier
Advantages of EQTEC Advanced Gasification Technology
Operational efficiency and sustainability
Commercially proven technology with high operational efficiency. We have created four installations, one with 10 years of live operating hours and process analytics
Environmental impact
Projects have the highest energy efficiency amongst waste-to-energy technologies and the lowest energy-from-waste technology environmental impact.
Low risk and high quality
Low risk and quick to install, we create additional value by ensuring high system availability, reliability and quality operational performance at each plant.
Versatile
Extensive versatility in successfully converting feedstock inputs into energy and fuel outputs.
Consistent standards
Accurate software modelling
Our unique and highly accurate software modelling and IoT monitoring platform make us the partner of choice for leading waste management stakeholders across Europe and the USA.
Our technology partners







